Total cost of asset ownership for titanium alloys tends to be lower due to its service life and reduced maintenance cost
Titanium alloys are recognized for its high strength-to-density ratio and superior corrosion resistance. Used in a variety of applications in the chemical processing industry titanium alloys demonstrate an extensive serviceable temperature range as well as corrosion resistance to processes such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid and chlorine chemicals.
Contamination is a leading cause of weld failure
Reactive metals such as titanium alloys can be a welding challenge based on their physical and chemical characteristics. The titanium alloy can have an oxidization reaction at ambient temperature leading to contamination of welds. Substances such as oils, paints, dirt and other debris can cause embrittlement and porosity. Although relatively similar to welding other alloys, it is imperative for titanium to follow strict procedure for clean welding, particularly in the field setting, to avoid contamination.
Accepted Welding Processes for Titanium
Titanium alloys are most widely welded using the gas tungsten-arc welding (GTAW), plasma arc welding (PAW) and gas metal-arc welding (GMAW) processes. Other methods such as electron beam and resistance welding are typically not associated with field titanium welding applications. Generally, GTAW has been viewed as a higher quality weld but slower process requiring high manual welder proficiency. Furthermore, PAW requires precise bevels to be machined with little to no variance from mismatch or root gaps.
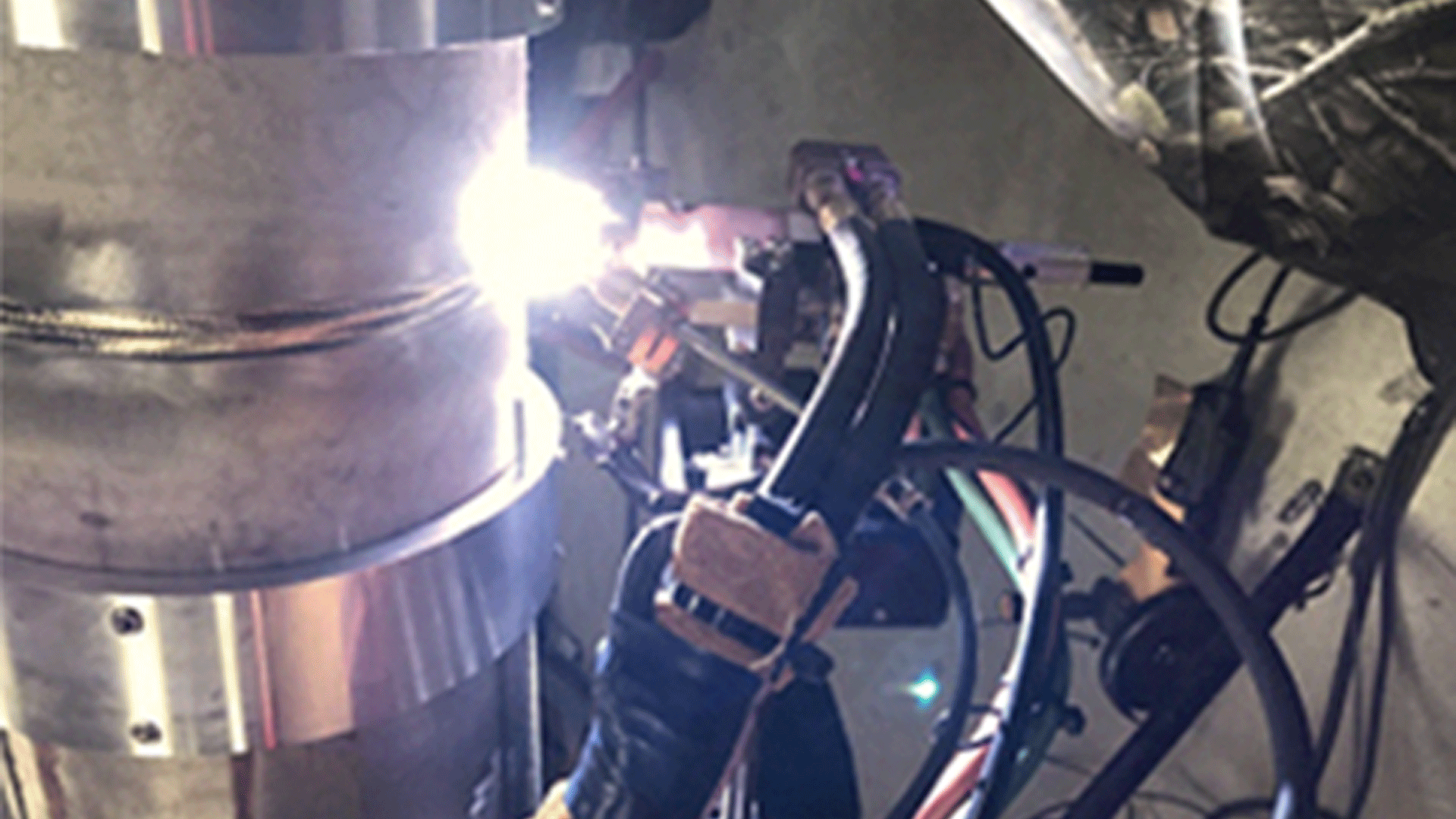
WSI’s HP GTAW™ Machine & Semi-Automatic Welding Process
By using a variety of industry best practices for titanium welding such as thorough cleaning of the base materials, properly cleaning filler wire, and wearing nitrile gloves WSI’s ASME certified and skilled craftsmen follow a strict protocol to mitigate contamination concerns. The HP GTAW™ process for titanium welding uses 99.995% purity argon shielding gas to the weldments, molten weld puddle and associated heat affected zones to prevent oxidation.
WSI’s machine HP GTAW™ welding technology combines unparalleled deposition rates with superior arc control. By utilizing a proprietary system of wire pre-heating, precise dabbing mechanics, and controlled waveforms the HP GTAW™ process decreases porosity, improves grain refinement and is significantly less susceptible to fit up imperfections in field joints. This provides superior weld quality with increased production rates with reduced risk of failure.
About WSI
Whether the titanium unit and equipment needs to be repaired as an emergency or during a planned turnaround, WSI has unparalleled innovative leadership in the nuclear, refining, power generation and petrochemical industries. Including titanium WPS, WSI has over 2000 ASME qualified procedures and over 1000 active welder certifications. Find out more about our engineered solutions and welding technologies at WSI.